- What is the primary function of the immune system?
- The immune system protects the body from pathogens and foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and toxins.
- Name the cells responsible for producing antibodies.
- B cells (or B lymphocytes) produce antibodies.
- Define antigen.
- An antigen is a molecule that can be recognized by the immune system, typically triggering an immune response.
- What are the two main types of adaptive immune responses?
- Cell-mediated immunity and humoral immunity.
- Name the cells responsible for engulfing and digesting pathogens and debris in the body.
- Phagocytes, such as macrophages and neutrophils, carry out phagocytosis.
- Define vaccination.
- Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the immune system’s production of antibodies, providing immunity against specific pathogens.
- Name the proteins secreted by cells to inhibit the spread of viral infections.
- Interferons.
- What is the role of T cells in the immune response?
- T cells play a central role in cell-mediated immunity, recognizing and destroying infected or abnormal cells.
- Define immunoglobulins.
- Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are proteins produced by B cells that recognize and bind to specific antigens.
- What is the function of the thymus gland in the immune system?
- The thymus gland is involved in the maturation and differentiation of T cells.
- Define autoimmune disease.
- Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the body’s own tissues.
- Name the process by which antibodies bind to antigens, marking them for destruction.
- Opsonization.
- What is the primary role of dendritic cells in the immune system?
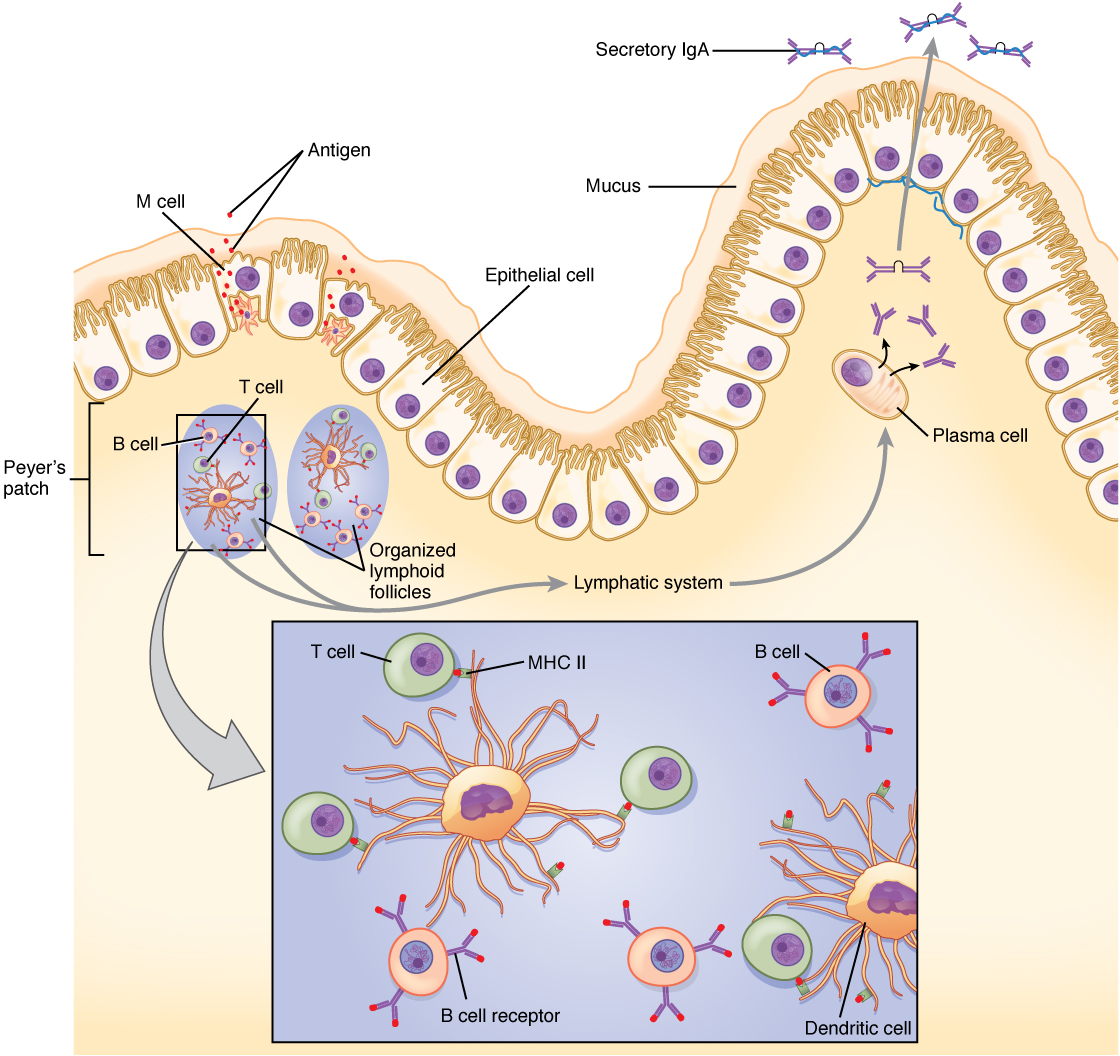
- Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells that capture, process, and present antigens to T cells, initiating adaptive immune responses.
- Define passive immunity.
- Passive immunity occurs when antibodies are transferred from one individual to another, providing immediate, short-term protection against a specific pathogen.
- Name the cells responsible for secreting histamine during allergic reactions.
- Mast cells.
- What is the function of memory B cells in the immune system?
- Memory B cells “remember” previous encounters with specific antigens, allowing for a quicker and more robust immune response upon re-exposure to the same antigen.
- Define immunodeficiency.
- Immunodeficiency refers to a weakened or impaired immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections and diseases.
- Name the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules involved in antigen presentation to T cells.
- MHC class I and MHC class II molecules.
- What is the role of natural killer (NK) cells in the immune system?
- NK cells play a critical role in the innate immune response by recognizing and destroying infected or abnormal cells, particularly those lacking MHC class I molecules.
- Define cytokines.
- Cytokines are small proteins secreted by immune cells that regulate the immune response by promoting inflammation, cell signaling, and cell differentiation.
- Name the process by which antibodies neutralize toxins produced by pathogens.
- Neutralization.
- What is the function of the spleen in the immune system?
- The spleen filters the blood, removes old or damaged red blood cells, and serves as a site for immune responses to blood-borne pathogens.
- Define antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
- Antigen-presenting cells are specialized immune cells, such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells, that capture, process, and present antigens to T cells to initiate adaptive immune responses.
- Name the type of T cells that suppress immune responses and prevent autoimmune reactions.
- Regulatory T cells (Tregs).
- What is the role of cytokines in inflammation?
- Cytokines regulate the inflammatory response by promoting the recruitment of immune cells to the site of infection or tissue damage and stimulating their activation.
- Define allergen.
- An allergen is a harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in individuals with allergies.
- Name the cells responsible for the production of antibodies during a secondary immune response.
- Memory B cells.
- What is the function of the lymph nodes in the immune system?
- Lymph nodes filter lymphatic fluid, trap foreign particles and pathogens, and facilitate interactions between immune cells during immune responses.
- Define antigenicity.
- Antigenicity refers to the ability of a molecule to stimulate an immune response by binding to specific receptors on immune cells.
- Name the type of hypersensitivity reaction mediated by IgE antibodies.
- Type I hypersensitivity (immediate hypersensitivity or allergic reactions).
- What is the function of complement proteins in the immune system?
- Complement proteins form part of the innate immune system and play a role in inflammation, opsonization, and cell lysis.
- Define inflammation.
- Inflammation is a protective response of the immune system to infection, injury, or tissue damage, characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain.
- Name the cells responsible for coordinating immune responses and regulating the activities of other immune cells.
- Helper T cells.
- What is the role of antibodies in agglutination?
- Antibodies bind to multiple antigens, causing them to clump together, facilitating their clearance by phagocytes.
- Define cross-reactivity.
- Cross-reactivity occurs when an antibody or T cell receptor recognizes and binds to similar antigens other than the one that induced the immune response.
- Name the process by which T cells undergo maturation and selection in the thymus gland.
- Thymic selection.
- What is the function of the bone marrow in the immune system?
- The bone marrow is the primary site of hematopoiesis, where blood cells, including immune cells, are produced and mature.
- Define adjuvant.
- An adjuvant is a substance added to vaccines to enhance the immune response, leading to a stronger and more prolonged immune response.
- Name the cells responsible for the production of antibodies specific to a particular pathogen.
- Plasma cells.
- What is the function of toll-like receptors (TLRs) in the immune system?
- Toll-like receptors recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and activate innate immune responses, including the production of cytokines and the upregulation of co-stimulatory molecules.
- Define immunotherapy.
- Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that harnesses the body’s immune system to fight diseases, such as cancer, allergies, and autoimmune disorders.
- Name the process by which antibodies and complement proteins coat pathogens, promoting their phagocytosis.
- Opsonization.
- What is the role of memory T cells in the immune system?
- Memory T cells “remember” previous encounters with specific antigens, allowing for a quicker and more robust immune response upon re-exposure to the same antigen.
- Define anaphylaxis.
- Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction characterized by systemic symptoms, including difficulty breathing, drop in blood pressure, and hives.
- Name the cells responsible for presenting antigens to T cells during cell-mediated immune responses.
- Antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells.
- What is the function of cytotoxic T cells in the immune response?
- Cytotoxic T cells recognize and destroy infected or abnormal cells by inducing apoptosis (cell death).
- Define primary immune response.
- The primary immune response is the initial immune response to an antigen, characterized by the activation and proliferation of lymphocytes and the production of antibodies.
- Name the cells responsible for providing long-term immunity following vaccination or infection.
- Memory B cells and memory T cells.
- What is the role of the lymphatic system in the immune response?
- The lymphatic system transports lymphatic fluid, immune cells, and antigens throughout the body, facilitating immune surveillance and immune responses.
- Define tolerance.
- Tolerance refers to the ability of the immune system to recognize and tolerate self-antigens, preventing immune reactions against the body’s own tissues.